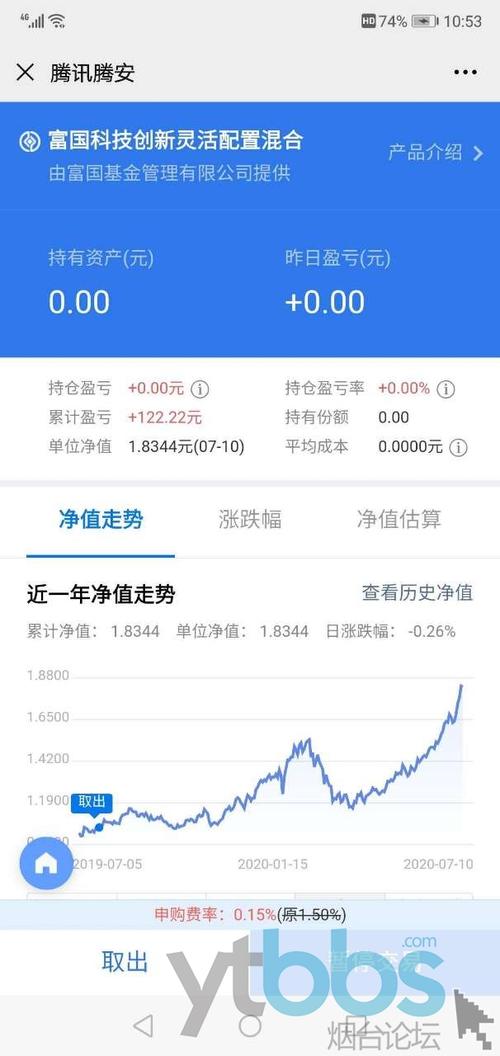
Net Asset Value (NAV) of a mutual fund is a critical metric for investors, as it reflects the fund's pershare market value. NAV is calculated by subtracting the fund's liabilities from its assets and dividing by the number of outstanding shares. Let's delve deeper into the significance of NAV and how it affects investors:
1. Calculation of NAV
To calculate the NAV of a mutual fund, you need two key pieces of information:
- Assets: These include all the securities, cash, and other holdings owned by the fund.
- Liabilities: These encompass all the debts and obligations owed by the fund, such as management fees and operating expenses.
The formula for calculating NAV is:
\[ NAV = \frac{{\text{Total Assets} \text{Total Liabilities}}}{{\text{Total Number of Outstanding Shares}}} \]
2. Importance of NAV
NAV serves as a crucial reference point for investors because:
- Valuation: It provides insight into the current value of each share of the mutual fund.
- Performance Measurement: Changes in NAV over time indicate the fund's performance. An increasing NAV suggests growth, while a decreasing NAV may indicate decline.
- Buying and Selling: Investors buy and sell mutual fund shares at NAV. However, sales charges or redemption fees may apply.
3. Factors Affecting NAV
Several factors influence a mutual fund's NAV:
- Market Fluctuations: Changes in the market value of the fund's holdings directly impact its NAV. For example, if the stock prices of the fund's investments rise, its NAV increases.
- Expenses: Fees and expenses, such as management fees and operational costs, reduce the fund's NAV.
- Distributions: When a fund distributes dividends or capital gains to shareholders, its NAV decreases accordingly.
4. Investment Strategies
Understanding NAV is essential for investors when devising their investment strategies:
- LongTerm Investment: Investors aiming for longterm growth should focus on the fund's performance relative to its NAV over time.
- Cost Considerations: Investors should evaluate a fund's expenses and fees, as they directly impact the fund's NAV and, consequently, the investor's returns.
- Diversification: Investing in funds with different NAVs and asset classes can help mitigate risks and enhance portfolio diversification.
5. Conclusion
Net Asset Value (NAV) is a fundamental metric for mutual fund investors, reflecting the pershare market value of the fund. By understanding NAV and its implications, investors can make informed decisions, devise effective investment strategies, and navigate the dynamic landscape of the financial markets.
